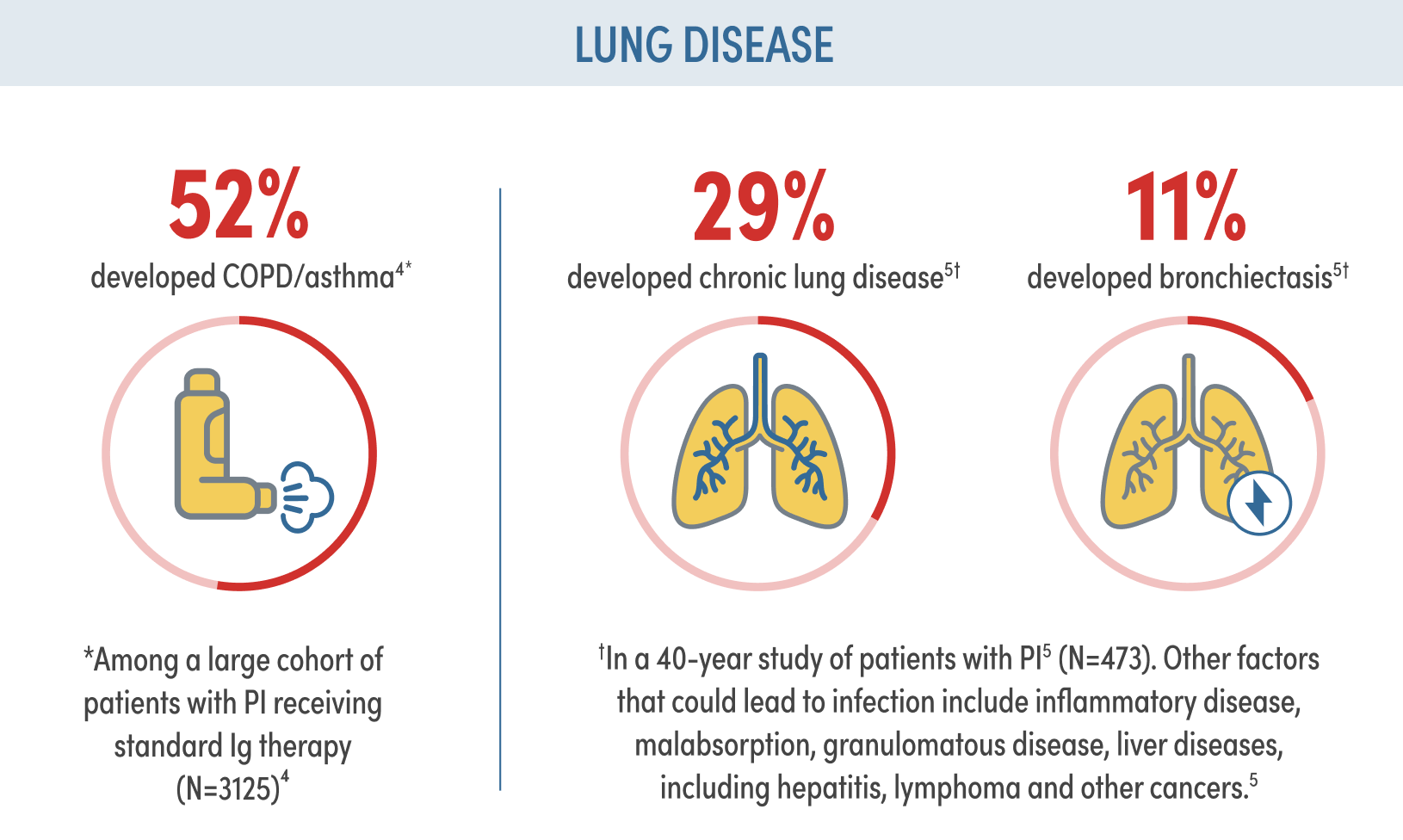
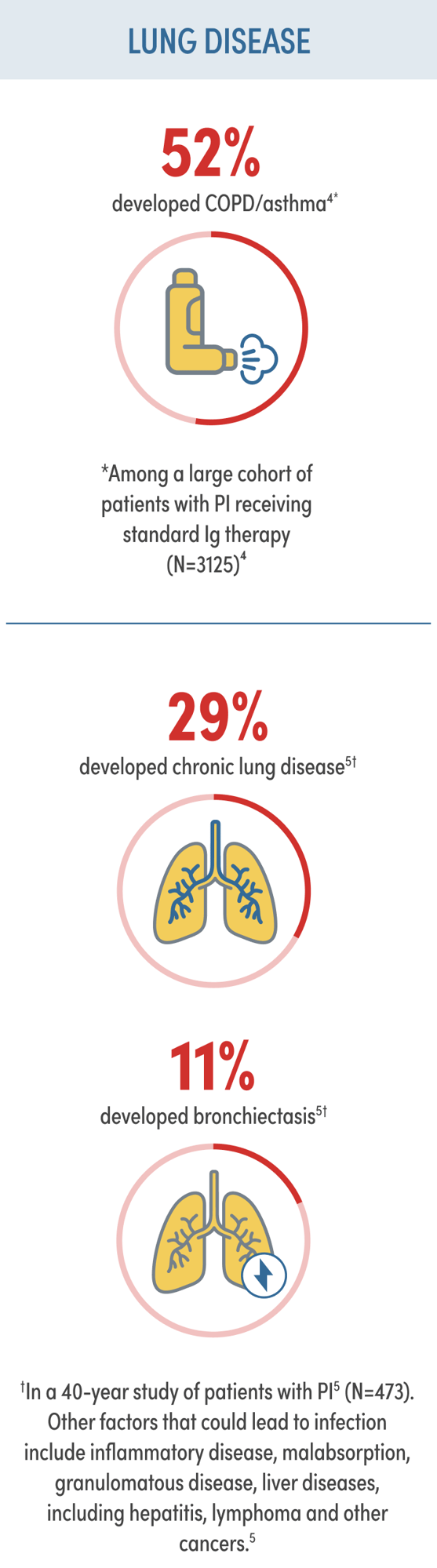
PI RISK AND IMPLICATIONS
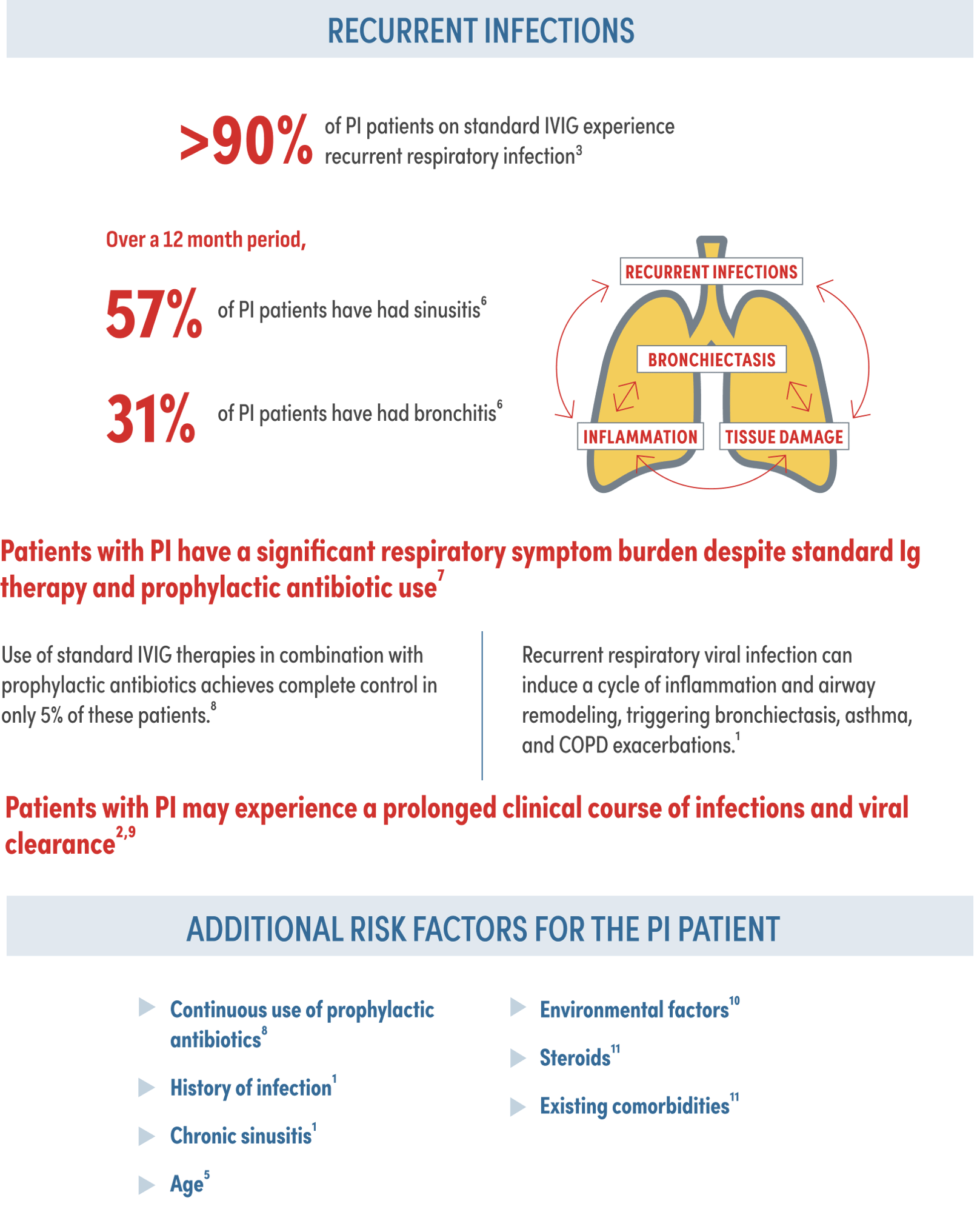
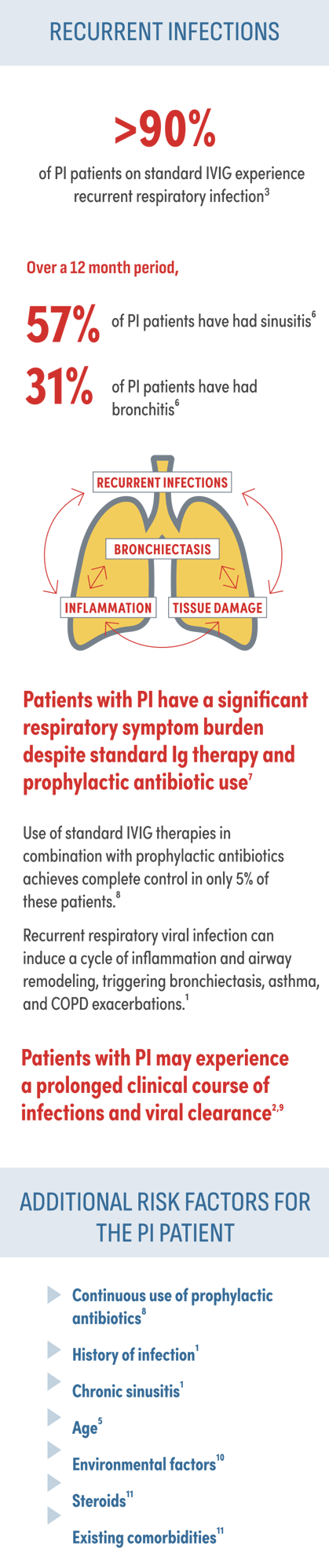
Despite standard Ig therapy, patients continue to experience recurrent respiratory infection and chronic lung disease1,2
Risk factors that complicate the approach to PI and impact survival include:
PI patients deserve an individualized treatment approach based on variation in clinical presentation
Despite standard Ig therapy, patients with PI experience significant reductions in their quality of life8
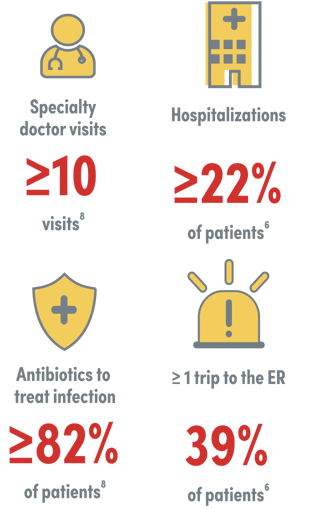
of PI patients still experience activity limitations annually despite IgRT according to the IDF survey8‡

Patients treated with standard IVIG continue to miss many days of work/school. On average, in a 12 month period patients missed the following days of work/school due to illness8§‖:
21.1 days of work
24 days of school
Based on the IDF surveys of adults with PI, a significant percentage of PI patients annually require the following6,8:
When selecting an Ig replacement therapy,
individual patient characteristics should be considered
‡Patients were asked, “During the past 12 months, how much has he/she been limited in work, play, or normal physical activity as a result of his/her health?” Answers were limited to individuals who currently use Ig replacement.8
§Patients were asked, “Not counting hospitalizations, how many days was the patient too sick to work, go to school, or perform usual activities in the past 12 months?” Answers were limited to individuals who currently use Ig replacement, including intravenous and subcutaneous Ig. Those who were retired or too disabled to work were excluded.8
‖Calculated standard mean of IVIG and SCIG.
#Answers include PI patients who are not on IgRT.
IDF=Immune Deficiency Foundation.
Indication
ASCENIV (immune globulin intravenous, human–slra) is a 10% immune globulin liquid for intravenous injection, indicated for the treatment of primary humoral immunodeficiency (PI) in adults and adolescents (12 to 17 years of age). PI includes, but is not limited to, the humoral immune defect in congenital agammaglobulinemia, common variable immunodeficiency (CVID), X linked agammaglobulinemia, Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome, and severe combined immunodeficiencies (SCID).
Important Safety Information for ASCENIV™
WARNING: THROMBOSIS, RENAL DYSFUNCTION AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
- Thrombosis may occur with immune globulin (IGIV) products, including ASCENIV. Risk factors may include: advanced age, prolonged immobilization, hypercoagulable conditions, history of venous or arterial thrombosis, use of estrogens, indwelling central vascular catheters, hyperviscosity, and cardiovascular risk factors. Thrombosis may occur in the absence of known risk factors.
- Renal dysfunction, acute renal failure, osmotic nephrosis, and death may occur with the administration of IGIV products in predisposed patients.
- Renal dysfunction and acute renal failure occur more commonly in patients receiving IGIV products containing sucrose. ASCENIV does not contain sucrose.
- For patients at risk of thrombosis, renal dysfunction or renal failure, administer ASCENIV at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration in patients before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity.
Contraindications
ASCENIV is contraindicated in:
- Patients who have had an anaphylactic or severe systemic reaction to the administration of human immune globulin.
- IgA-deficiency patients with antibodies to IgA and a history of hypersensitivity.
Warnings and Precautions
Severe hypersensitivity reactions may occur with IGIV products, including ASCENIV. In case of hypersensitivity, discontinue ASCENIV infusion immediately and institute appropriate treatment. Patients with known antibodies to IgA may have a greater risk of developing potentially severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions.
Thrombosis may occur following treatment with immunoglobulin products and in the absence of known risk factors. Consider baseline assessment of blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity and ensure adequate hydration before administration. For patients at risk of thrombosis, administer ASCENIV at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity.
Acute renal dysfunction/failure, osmotic nephrosis, and death may occur upon use of human IGIV products. Ensure that patients are not volume depleted before administering ASCENIV. Periodic monitoring of renal function and urine output is particularly important in patients judged to be at increased risk of developing acute renal failure. Assess renal function, including measurement of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine, before the initial infusion of ASCENIV and at appropriate intervals thereafter. Discontinue ASCENIV if renal function deteriorates. In at-risk patients, administer ASCENIV at the minimum infusion rate practicable.
Hyperproteinemia, increased serum viscosity, and hyponatremia or pseudohyponatremia may occur in patients receiving IGIV treatment, including ASCENIV. It is critical to clinically distinguish true hyponatremia from a pseudohyponatremia that is associated with or causally related to hyperproteinemia. Treatment aimed at decreasing serum free water in patients with pseudohyponatremia may lead to volume depletion, a further increase in serum viscosity, and a possible predisposition to thrombotic events.
Aseptic meningitis syndrome (AMS) may occur with IGIV treatments, including ASCENIV. AMS usually begins within several hours to 2 days following IGIV treatment. AMS may occur more frequently in association with high doses (2 g/kg) and/or rapid infusion of IGIV. Conduct a thorough neurological examination on patients exhibiting signs and symptoms of AMS, including cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) studies, to rule out other causes of meningitis.
IGIV products, including ASCENIV, may contain blood group antibodies that can act as hemolysins and induce in vivo coating of red blood cells (RBCs) with immunoglobulin, causing a positive direct antiglobulin reaction and hemolysis. Monitor patients for clinical signs and symptoms of hemolysis, including appropriate confirmatory laboratory testing.
Noncardiogenic pulmonary edema may occur with IV administered IG. Monitor patients for pulmonary adverse reactions. If suspected, perform appropriate tests for presence of anti-neutrophil antibodies in both product and patient serum. May be managed using oxygen therapy with adequate ventilatory support.
Because ASCENIV is made from human blood, it may carry a risk of transmitting infectious agents, e.g., viruses, the variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (vCJD) and theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent. All infections suspected by a physician to possibly have been transmitted by this product should be reported to ADMA Biologics at (1-800-458-4244).
After infusion of immunoglobulin, the transitory rise of the various passively transferred antibodies in the patient’s blood may yield positive serological testing results, with the potential for misleading interpretation. Passive transmission of antibodies to erythrocyte antigens (e.g., A, B, and D) may cause a positive direct or indirect antiglobulin (Coombs’) test.
Adverse Reactions
The most common adverse reactions to ASCENIV (≥5% of study subjects) were headache, sinusitis, diarrhea, gastroenteritis viral, nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, bronchitis, and nausea.
You are encouraged to report side effects of prescription drugs to ADMA Biologics at 1-800-458-4244 or the FDA. Visit www.fda.gov/MedWatch or call 1-800-FDA-1088.
For additional safety information about ASCENIV, please see full Prescribing Information.